The securities research information involved in this subscription number is compiled by the fixed-income research team of Everbright Securities (601788), which is only for the professional investors and customers of Everbright Securities, and is used for the communication of research information and research opinions under the new media situation. Customers who are not professional investors of Everbright Securities, please do not subscribe, receive or use any information in this subscription number. It is difficult to set access rights for this subscription number. Please forgive me if it causes you any inconvenience. Everbright Securities Research Institute will not regard relevant personnel as customers of Everbright Securities because they pay attention to, receive or read the content pushed by this subscription number.
Author of this article
Zhang Xu/Wei Weixiao
abstract
The disposal of creditor’s rights of Baoshang Bank has caused us to think: Can the financial supervision department put forward higher supervision requirements for banks, so that they can reserve enough internal bail-out funds to absorb losses in the process of risk disposal?
TLAC is the abbreviation of Total Loss-Absorbing Capacity, which refers to the sum of various capital or debt instruments that can absorb bank losses through write-down or share conversion when G-SIBs enters the disposal procedure, that is, the ability of "internal bail-out".
How can we replenish TLAC capital as soon as possible? We believe that regulatory capital can be supplemented and debt instruments that are not included in regulatory capital but meet the requirements of TLAC can be issued.
Perpetual bonds of commercial banks can be a breakthrough to supplement tier-one capital. Today (July 26th), ICBC is issuing 80 billion yuan of open-ended bonds.
Since the beginning of this year, in order to issue perpetual bonds smoothly, the People’s Bank of China and China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission have also provided relevant policies. For example, the People’s Bank of China has created CBS, and primary dealers can use the qualified perpetual bonds they hold to exchange them for central bank bills.
In addition to using existing tools to supplement regulatory capital, TLAC can also be supplemented by some innovative capital tools.
Most banks in the United States meet the regulatory requirements of TLAC by issuing senior bonds by holding companies, while banks in EU countries tend to use senior non-priority bonds to supplement TLAC capital.
1. Thoughts on the disposal scheme of creditor’s rights of contractor bank.
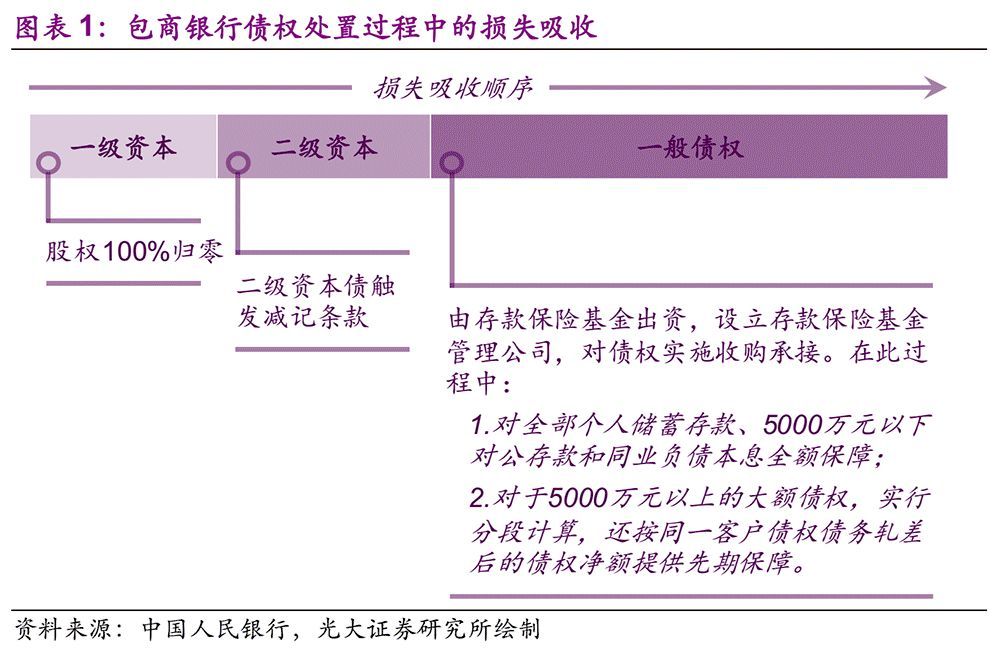
The capital of commercial banks plays a role in absorbing losses before ordinary creditors. For example, in the process of disposing the creditor’s rights of contractor banks, the losses are first absorbed by the original shareholders and the holders of secondary capital bonds. Due to the credit crisis of Baoshang Bank, even if the equity is cleared 100%, it still can’t absorb all the losses, so some subsequent losses need to be absorbed by the deposit insurance fund management company and some creditors.
How much loss should the deposit insurance fund bear? In order to avoid risks, the Deposit Insurance Fund fully guarantees the principal and interest of all personal savings deposits, corporate deposits of less than 50 million yuan and interbank liabilities through debt acquisition, corresponding to 5.2 million depositors, 25,000 enterprises and interbank institutions respectively. Obviously, the part undertaken by the deposit insurance fund far exceeds the limit of 500,000 yuan stipulated in the Deposit Insurance Ordinance, and its initiative to bear losses is mainly to protect the interests of ordinary creditors as much as possible.
However, this has also triggered our new thinking: the failure of commercial banks has negative macro-spillover, and in order to prevent systemic risks, the government has to use public funds to provide assistance. Then, is it possible to put forward higher regulatory requirements for banks, so that they can reserve enough internal bail-out funds to absorb losses during the disposal process, instead of relying on external public funds for assistance?
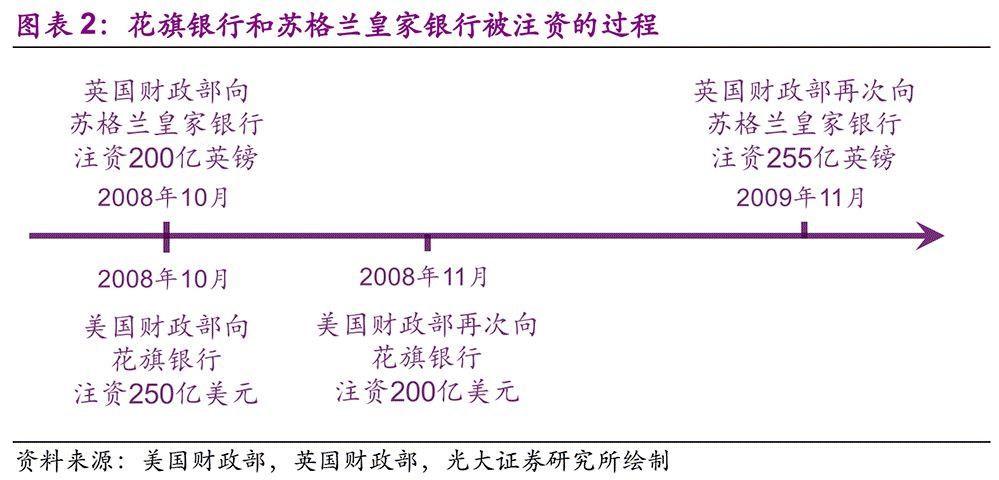
In fact, the problem of "negative macro spillover" is not unique to China, and the more important the bank, the greater its spillover, which is called "too big to fail". During the international financial crisis in 2008, the American and British governments were worried that the bankruptcy of Citibank and Royal Bank of Scotland would lead to systemic risks, so they injected 45 billion dollars and 45.5 billion pounds into the two banks respectively.
Such external assistance with public funds will not only increase the burden on taxpayers, but also lead to moral hazard of banks. In order to solve this problem, the FSB (Financial Stability Board) issued the Key Elements of Effective Disposal Mechanism of Financial Institutions at the G20 Cannes Summit in 2011, and put forward the goal of "internal bail-out" instead of "external assistance" of public funds in times of crisis. In November, 2015, FSB issued the Principles and Clauses of Loss Absorption and Capital Reorganization Ability in the Disposal of G-SIBs (referred to as TLAC Clause), which put forward higher requirements for the loss absorption ability of G-SIBs (global systemically important bank) than Basel III.
2. What is TLAC?
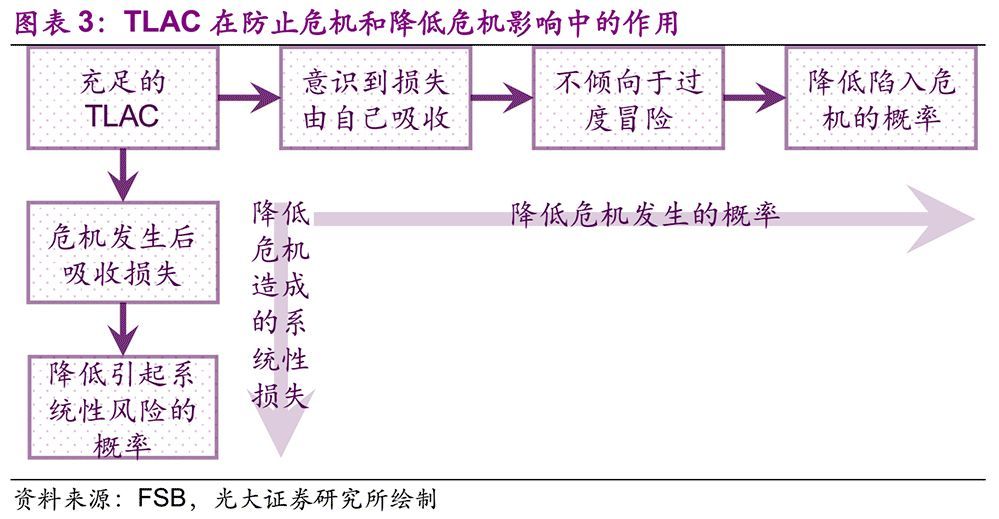
"TLAC" in the above-mentioned TLAC Clause is the abbreviation of Total Loss-Absorbing Capacity, which refers to the sum of various capital or debt instruments that can absorb bank losses through write-down or share conversion when G-SIBs enters the disposal procedure, that is, the ability of "internal bail-out". A higher TLAC ensures that banks have sufficient capacity to absorb losses when they enter the disposal procedure, thus reducing the probability that "too big to fail" banks will "fail" in a crisis and cause systemic risks. In addition, the "internal bail-out" model helps to encourage bank shareholders and management to increase risk management and reduce the possibility of excessive risk taking and falling into crisis.
According to the TLAC Clause, qualified TLAC tools need to meet the following criteria at the same time: 1. Paid-in; 2. Unsecured; 3. The ability to absorb losses in the process of disposal will not be weakened by the right of offset and net liquidation; 4. The remaining term of the contract is not less than one year or perpetual (no expiration date); 5. There is no investor’s right to sell back in the coming year; 6. No funds shall be provided directly or indirectly by the disposal entity or its related parties, unless approved by the regulatory authorities of the home country and the host country.
At the same time, qualified TLAC instruments cannot be excluded liabilities, that is, they cannot be any of the following liabilities: 1. Deposits protected by deposit insurance; 2. Demand deposits and deposits with an original term of less than one year; 3. Liabilities arising from derivatives; 4. Debt instruments with derivative linkage characteristics, such as capital preservation bills; 5. Liabilities arising outside the contract, such as tax obligations; 6. Liabilities (such as secured liabilities) stipulated in the bankruptcy law that are paid before senior unsecured creditors; 7. Liabilities excluded from internal bail-out by law or unable to be written down or converted into shares by relevant disposal authorities.
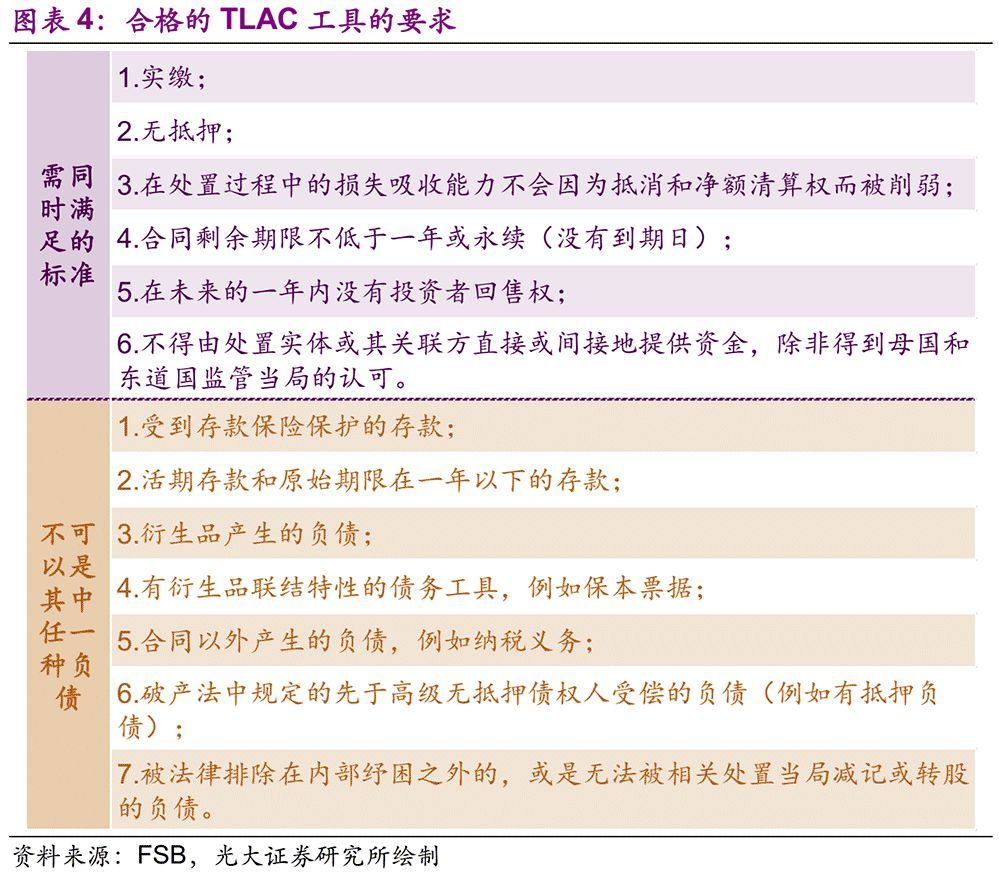
Qualified TLAC tools must absorb losses before being excluded from liabilities, so as to ensure the disposal ability of G-SIBs. In fact, the other side of loss absorption preposition is the secondary in compensation, and the secondary attribute can be realized in the following three ways:
1. contractual subordination: it is agreed in the form of contract that the TLAC instrument is subordinated to the excluded liabilities in the disposal entity table.
2. statutory subordination: In the statutory creditor hierarchy, the TLAC instrument is lower than the excluded liabilities in the disposal entity table.
3. structural subordination: TLAC instruments are issued by a disposal entity (such as a holding company) with no excluded liabilities on the balance sheet.
For example, in the terms of the bond, it is agreed that "the repayment order of the principal of the current bond and the interest payment order are after the depositor and the general creditor", which is the secondary agreement mentioned above, and banks in EU countries tend to use this method. The mode of issuing bonds by non-operating holding companies in the United States is the secondary structure mentioned above. In this mode of secondary structure, the excluded liabilities of subsidiaries are paid off first, and the bonds of holding companies play the role of loss absorption.
3. Applicable objects of TLAC
Basel III applies to all banks, while TLAC applies to G-SIBs. The list of G-SIBs is published by FSB every November. In November 2018, there were 29 banks in groups 1-4, corresponding to 1%-2.5% additional capital. At present, the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, Bank of China, Agricultural Bank of China and China Construction Bank are on the list, among which Agricultural Bank of China and China Construction Bank are in the first group, which are applicable to 1.0% additional capital, while Bank of China and ICBC are in the second group, which are applicable to 1.5% additional capital.
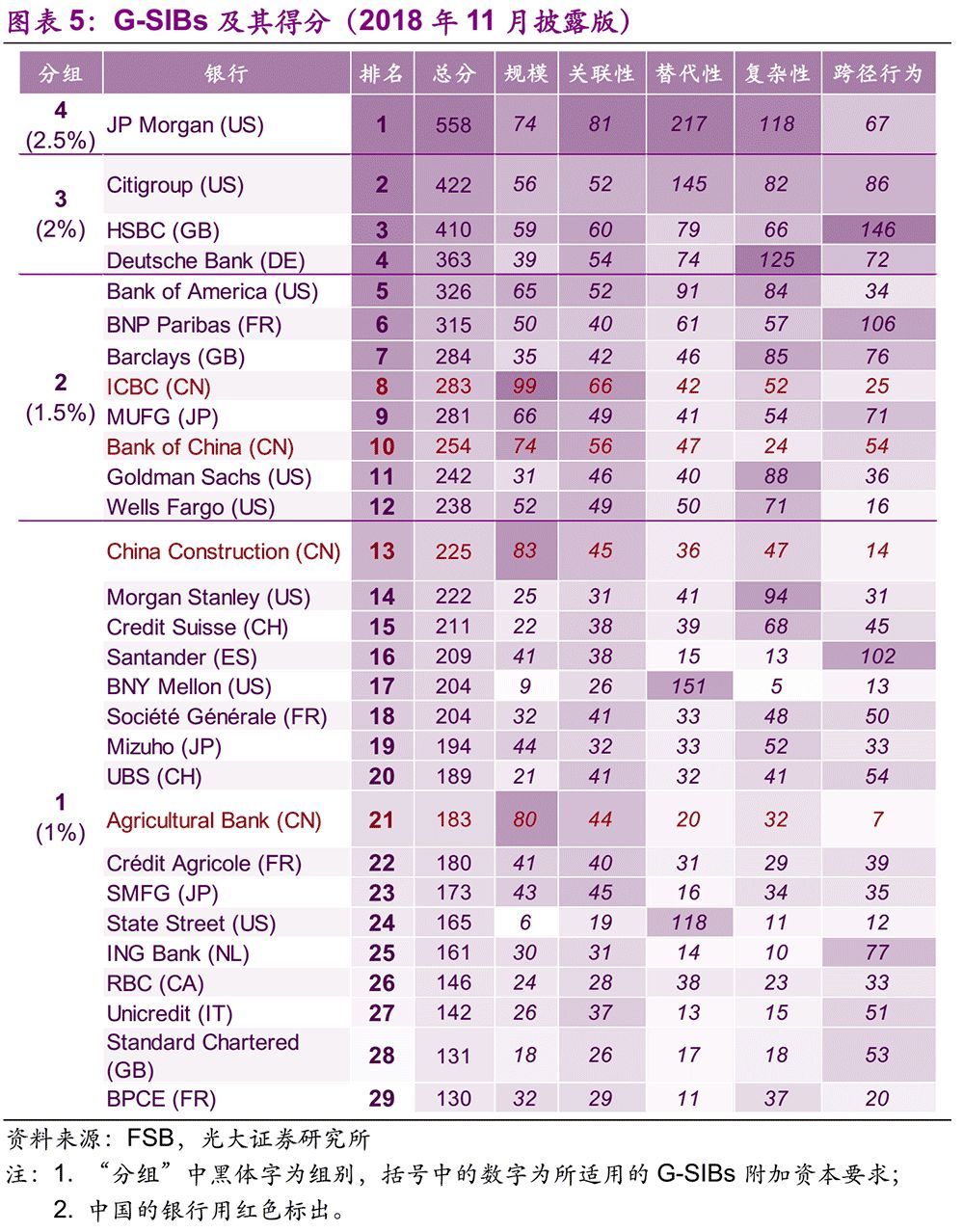
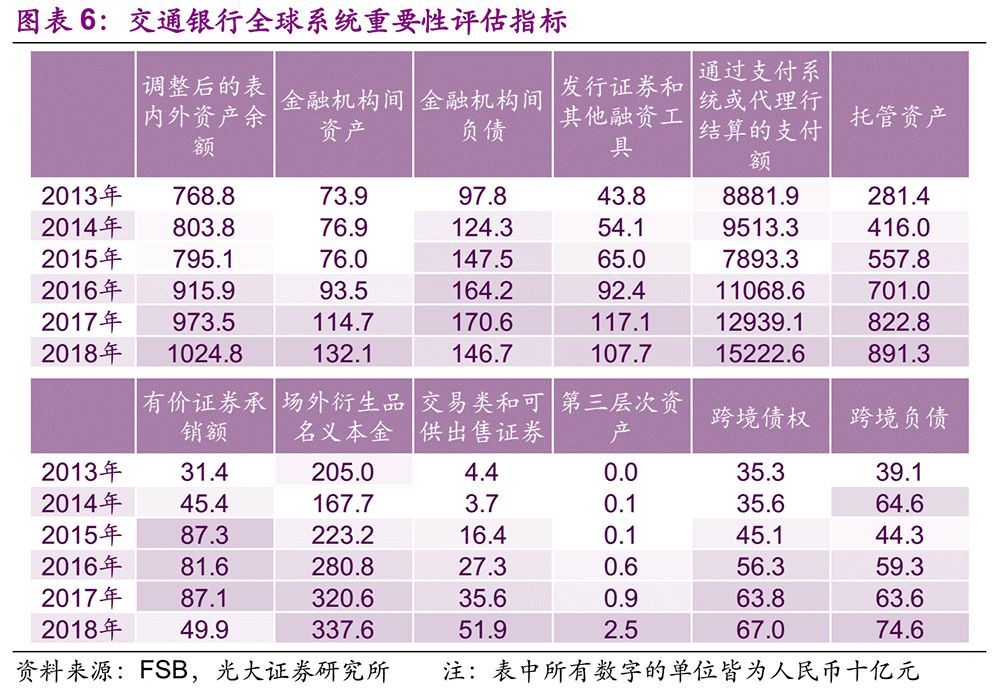
According to FSB rules and practical experience, those with a total score of 130 are more likely to be selected for G-SIBs. (Among the 29 G-SIBs selected in November, 2018, the lowest total score was BPCE, and its score was 130. The Bank of Communications is very close to the above standards. In the results disclosed in November 2018, the total score of the bank was 118, ranking 31 ST.
The results disclosed by FSB in November 18 correspond to 17 years’ data, and the results to be disclosed in November 19 correspond to 18 years’ data. We find that the data of most subjects of Bank of Communications have improved to varying degrees in the past 18 years. Among them, the highest increase rate is the third-tier assets, with the data of 910 million yuan in 17 years and 2.55 billion yuan in 18 years, an increase of 1.8 times. In addition, assets between financial institutions, payments settled through payment systems or correspondent banks, and cross-border liabilities have also increased by more than 15% respectively. Obviously, according to the current growth rate, it is a high probability that Bank of Communications will be included in G-SIBs in the next few years.
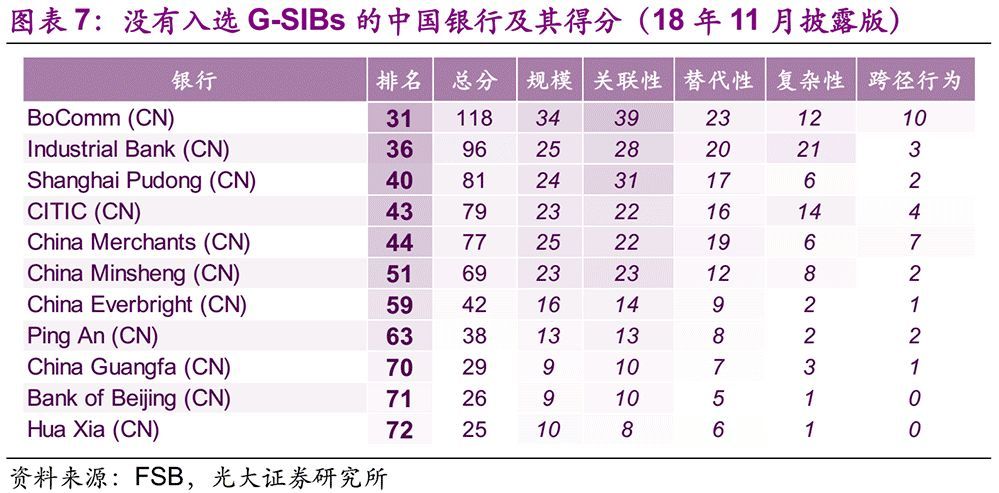
The score and ranking of Industrial Bank (601166) are not far from those of Bank of Communications, with 96 ranking 36. Next, the rankings of Shanghai Pudong Development Bank (600,000), China CITIC Bank (601,998) and China Merchants Bank (600,036) are relatively close, ranking 40th, 43rd and 44th respectively. The scores of Minsheng Bank (600016), China Everbright Bank (601818), Ping An Bank (00001), Guangfa Bank, Bank of Beijing (601169) and Huaxia Bank (600015) are all below 50% of the threshold of G-SIBs 130, so it is less likely to be recognized as G-SIBs in a short time.
The minimum TLAC requirements apply to every disposal entity in every G-SIB. The disposal entity here refers to the entity to which the disposal tool is applied in the G-SIB disposal strategy. According to different disposal strategies, the disposal entity can be the parent company, the intermediate or final holding company and the operating subsidiary. Moreover, a G-SIB can own one or more disposal entities.
A disposal entity and all entities owned and controlled by this disposal entity are regarded as a disposal group. It should be noted here that the above-mentioned entity owned or controlled should not be a disposal entity, and each disposal entity and the entity owned or controlled by it can only belong to one disposal group.
In addition, within a disposal entity, the direct or indirect subsidiaries that meet the requirements form an important disposal subgroup. In order to facilitate the cooperation between the authorities of the home country and the host country and realize the effective cross-border disposal strategy, FSB requires the appropriate allocation of loss absorption and capital reorganization capabilities within the disposal group. In view of this, FSB puts forward the requirements of internal TLAC for the important sub-groups of G-SIB. The minimum internal TLAC standard is 75%-90% of the minimum external TLAC standard.
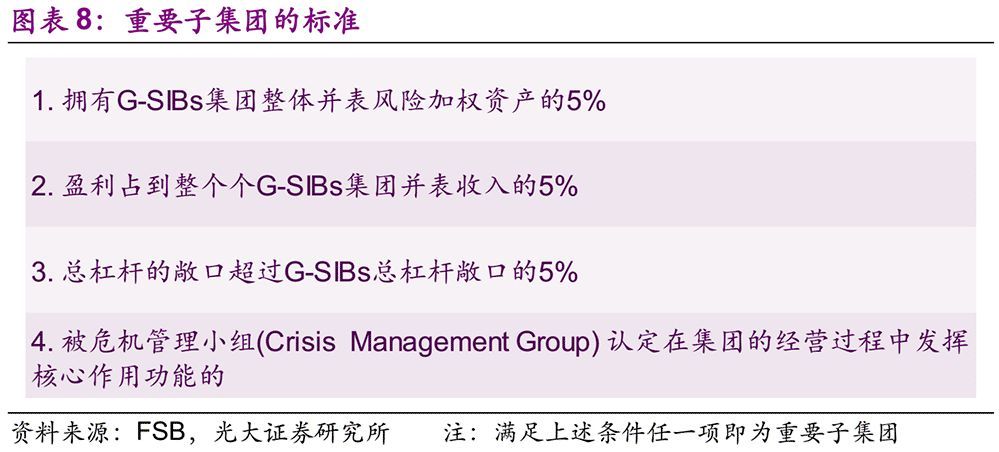
4. TLAC regulatory requirements
FSB formulates the most basic requirements for G-SIBs, including TLAC requirements based on risk-weighted assets and TLAC requirements based on total assets exposed to risk (i.e. leverage ratio). In addition to the requirements of FSB, the regulatory authorities of various countries or regions may put forward additional requirements for banks according to local actual conditions, and the specific standards shall be decided by the local regulatory authorities themselves.
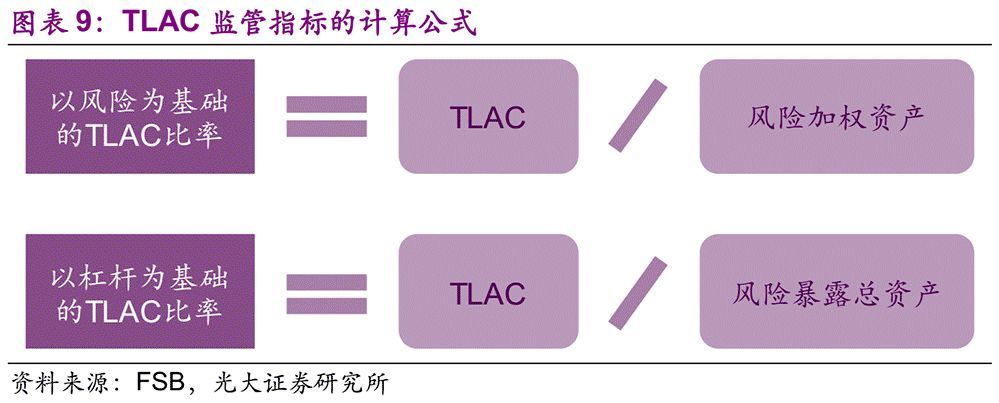
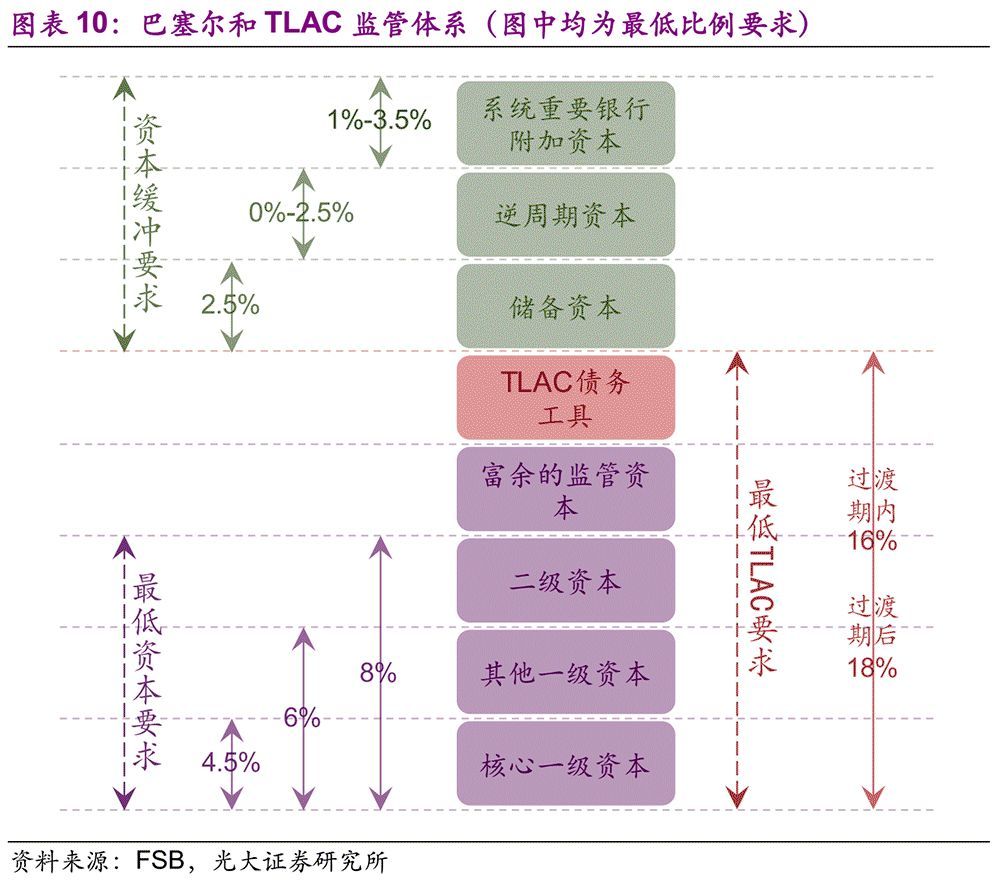
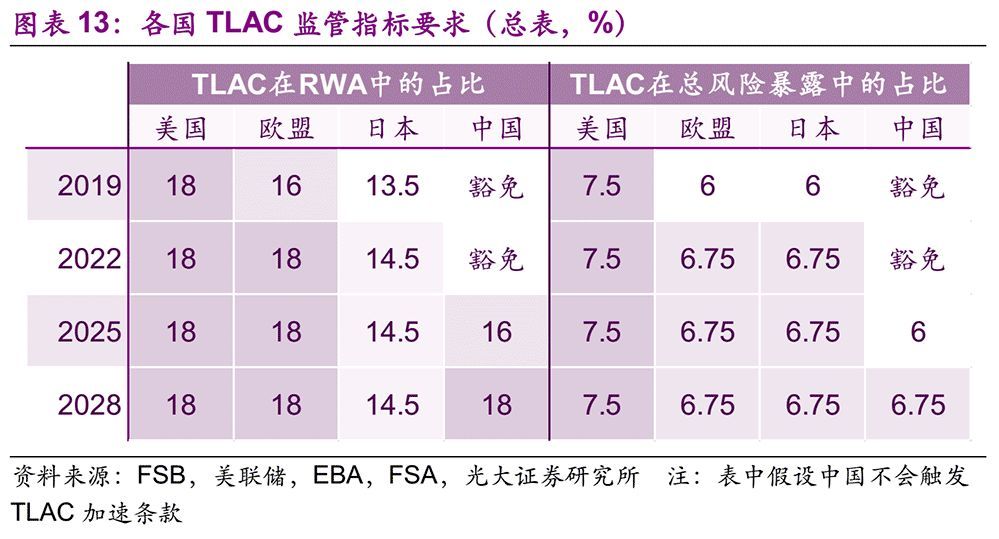
The TLAC Clause requires that for banks that become G-SIBs before the end of 2015, the TLAC shall account for no less than 16% of risk-weighted assets and the leverage ratio shall be no less than 6% from January 1, 2019; From January 1, 2022, the above two proportions will be increased to 18% and 6.75% respectively. In addition, G-SIBs also needs to meet the requirements of buffer capital, including reserve capital (2.5%), countercyclical capital (0-2.5%) and additional capital of G-SIBs (1-3.5%). For banks that become G-SIBs between 2016 and the end of 2018, they need to meet the above requirements from January 1, 2022; For banks that become G-SIBs after the end of 2018, they need to meet the requirements within 36 months after becoming G-SIBS.
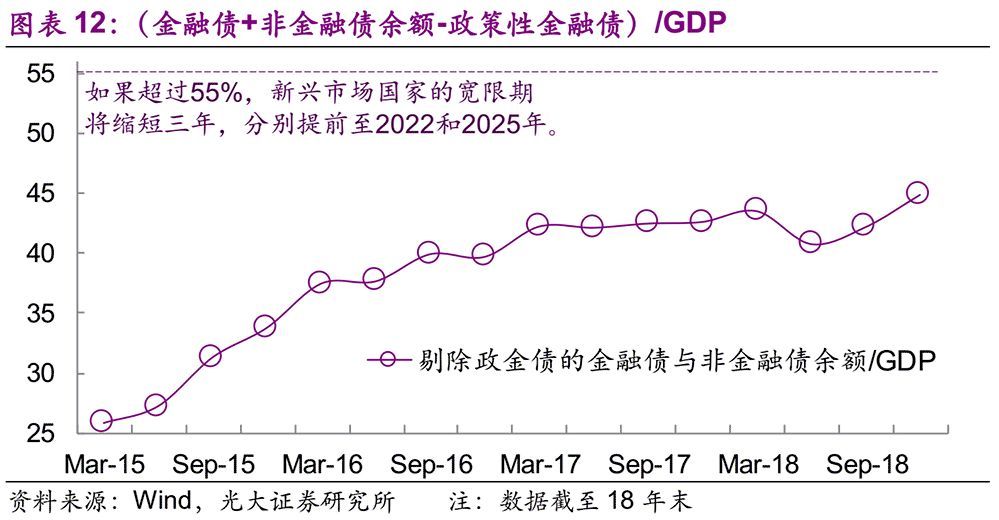
Considering the actual situation of emerging market countries, FSB gives them a grace period of six years, that is, the time to meet the standards is extended from 2019 and 2022 to 2025 and 2028. (Note: In fact, up to now, only China’s banks have been selected as G-SIBs among emerging market countries. However, there is an accelerated condition for this grace period: if the balance of financial and non-financial corporate bonds (excluding policy banks) in emerging market countries accounts for more than 55% of the country’s GDP within five years after the publication of the TLAC Clause, the grace period will be shortened by three years and advanced to 2022 and 2025 respectively.
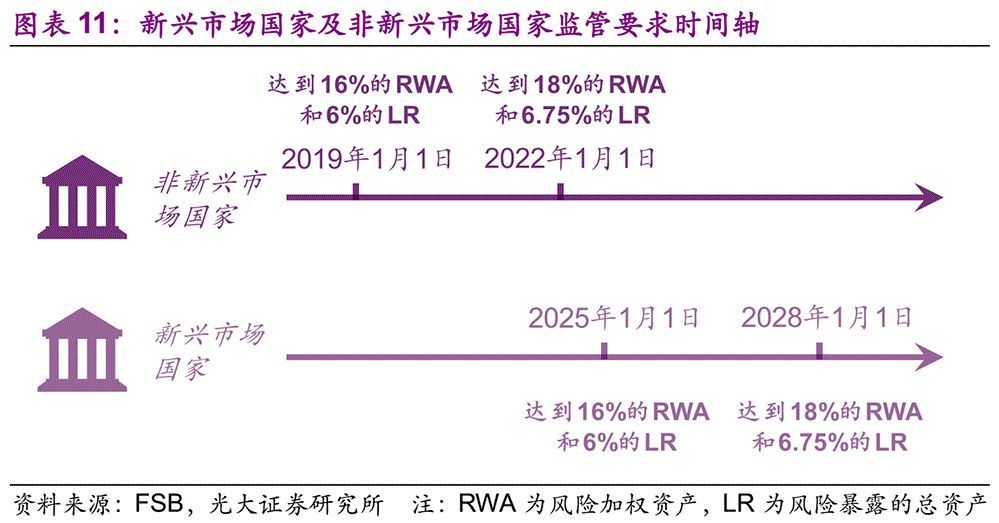
The TLAC clause of FSB was published in November 2015, so the final judgment of the accelerated clause will be in November 2020, and the data at the end of 2019 will be used for this judgment. By the end of 2018, the ratio of the balance of financial bonds and non-financial bonds excluding political bonds to GDP in China was close to 50%. If we extrapolate linearly at the current growth rate, the above ratio was very close to the threshold of 55% at the end of 2019.
In addition to the above-mentioned mandatory provisions, FSB also put forward the regulatory expectation in the TLAC Clause, that is, it is expected that the standard TLAC debt instruments will account for no less than 33% of the total capital of TLAC. This regulatory expectation is to ensure that G-SIBs has sufficient capital absorption losses when it enters the disposal procedure. According to the RAW standard of 16%, FSB expects the debt instruments in TLAC capital to account for no less than 5.28% of RAW.
At the same time, the TLAC Clause stipulates that if the relevant government departments promise in advance to reorganize the capital, bear the cost of the disposal fund or provide temporary disposal funds during the disposal of G-SIBs, the minimum requirements of TLAC can be reduced to some extent. For example, due to the commitment of deposit insurance system in Japan, the minimum TLAC requirement can be exempted: when the minimum TLAC requirement is 16%, it can be exempted from 2.5% (reduced to 13.5%); When the minimum requirement of TLAC is 18%, 3.5% can be exempted (reduced to 14.5%).
In addition, in order to reduce the cross-infection of risks in the banking system, the TLAC Clause also puts forward the deduction requirements for holding TLAC tools. Since then, it has been further clarified in the Basel III framework that the bank’s investment in non-capital TLAC tools issued by G-SIBs should be deducted from its own tier 2 capital.
The regulatory authorities in various countries and regions may put forward additional requirements for banks on the basis of FSB requirements according to local actual conditions. At present, there are some differences in the regulatory requirements of the United States, Japan and the European Union, which we will elaborate in the next part.
5. Implementation of TLAC in USA, Japan and EU
5.1. Implementation of TLAC in the United States
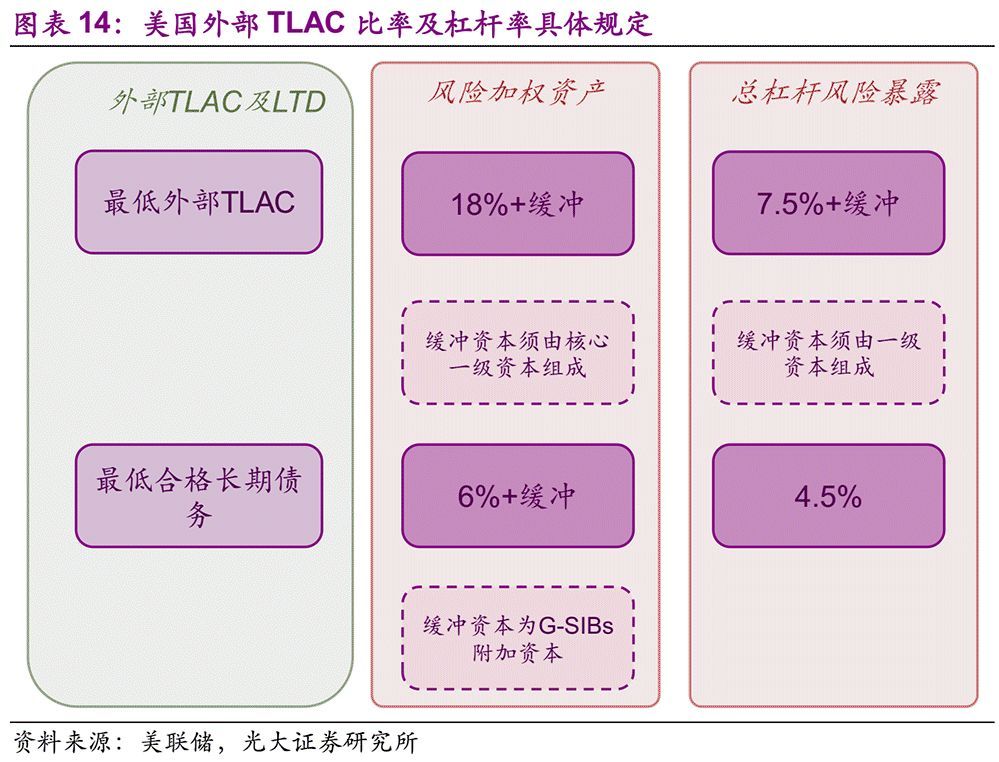
In December 2016, the Federal Reserve finalized the American version of the TLAC rules, which are applicable to the global systemically important bank holding companies (covered BHCs) in the United States and the important intermediate holding companies (covered IHCs) of foreign banks in the United States. The US TLAC rules formulated by the Federal Reserve are obviously stricter than the requirements of the FSB. For external TLAC, the difference between the minimum requirements of the Federal Reserve and the FSB is mainly reflected in the following three points: the transition period is cancelled, the leverage ratio is higher, and the hard requirements for long-term debt are increased.
1. Cancel the transition period: In the requirements of FSB, the period from 2019 to 2022 is a transition period. From 2022, the ratio of TLAC to risk-weighted assets and total risk exposure is not less than 18% and 6.75%, while only 16% and 6% are required during the transition period. TLAC in the United States canceled the transition period arrangement, requiring that it should not be lower than the final level required by FSB from 2019. (Note: The requirement of the Federal Reserve for leverage ratio is higher than that of the FSB’s TLAC. )
2. Increase the leverage ratio: FSB requires the leverage ratio to be greater than 6%, while in the Federal Reserve version of TLAC, it is obviously more stringent to require the leverage ratio to be greater than 7.5% plus 2% capital buffer.
3. Put forward the requirements of Ltd.: FSB only puts forward the regulatory expectations for the proportion of debt instruments, while the Federal Reserve puts forward mandatory regulatory requirements for the scale of long-term debt instruments. According to the requirements of the Federal Reserve, from 2019, the ratio of LTD/RWA (that is, the ratio of long-term debt instruments to risk-weighted assets) should be greater than 6% (in addition, G-SIBs has additional capital buffer requirements), and the total assets of LTD/ risk exposure should be greater than 4.5%.
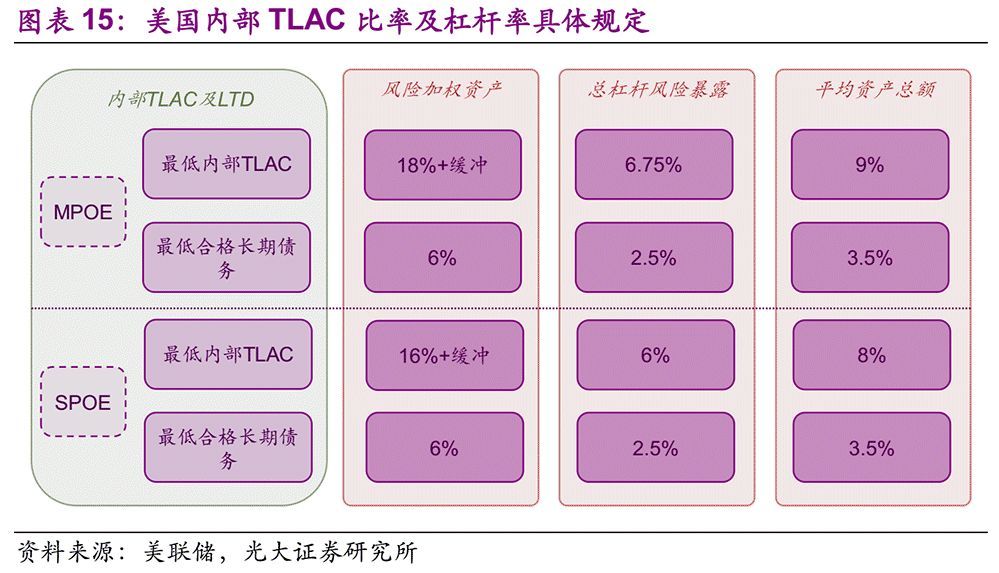
For internal TLAC, the Federal Reserve has put forward different requirements according to the nature of intermediate holding companies and different implementation strategies:
1. The intermediate holding company is the disposal entity, and the MPOE strategy (multi-point disposal entity strategy) is applicable: the Federal Reserve requires that the ratio of TLAC to risk-weighted assets and total risk exposure should be no less than 18% and 6.75%, which is consistent with the external TLAC of the corresponding banks in the United States (the internal TLAC requires lower leverage ratio), and the ratio of TLAC to average total assets should be no less than 9% (that is, Tier 1 capital leverage ratio). The requirements of the Federal Reserve for LTD are not less than 6%, 2.5% and 3.5% of risk-weighted assets, total risk exposure and average total assets.
2. The intermediate holding company is not a disposal entity, and the SPOE strategy (single disposal entity strategy) applies: the Federal Reserve requires that the ratio of TLAC to risk-weighted assets and total risk exposure should be no less than 16% and 6%, and the ratio of TLAC to average total assets should be no less than 8%. The requirements of the Federal Reserve for LTD are not less than 6%, 2.5% and 3.5% of risk-weighted assets, total risk exposure and average total assets.
5.2. TLAC implementation in Japan
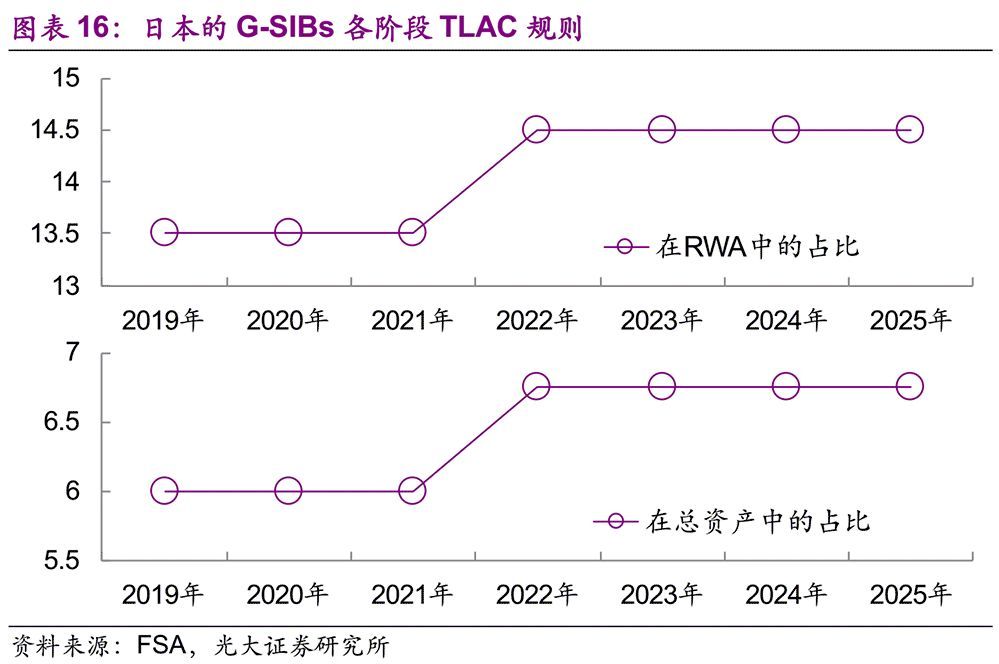
In the TLAC requirements formulated by the Financial Services Agency of Japan (FSA), it is considered to extend the scope of supervision to some D-SIBs, such as Nomura Holdings, Daiwa Securities, Japan Central Agriculture and Forestry Treasury, and Sumitomo Mitsui Trust Holding Company. Other regulated banks are called "Covered SIBs" together with G-SIBs in Japan. At present, there are four Covered SIBs in Japan, namely Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group, Mizuho Financial Group, Sumitomo Mitsui Financial Group and Nomura Holdings. The first three are G-SIBs recognized as of November 2018, and these three banks need to meet FSB standards from March 1, 2019. Nomura Holdings, as a domestic D-SIB in Japan, needs to meet the corresponding standards in two years (2021 and 2024). In addition, Japan’s TLAC rules have been implemented since March 31, 2019, which is slightly different from January 1, 2019 stipulated by FSB.
5.3. Implementation of TLAC in EU
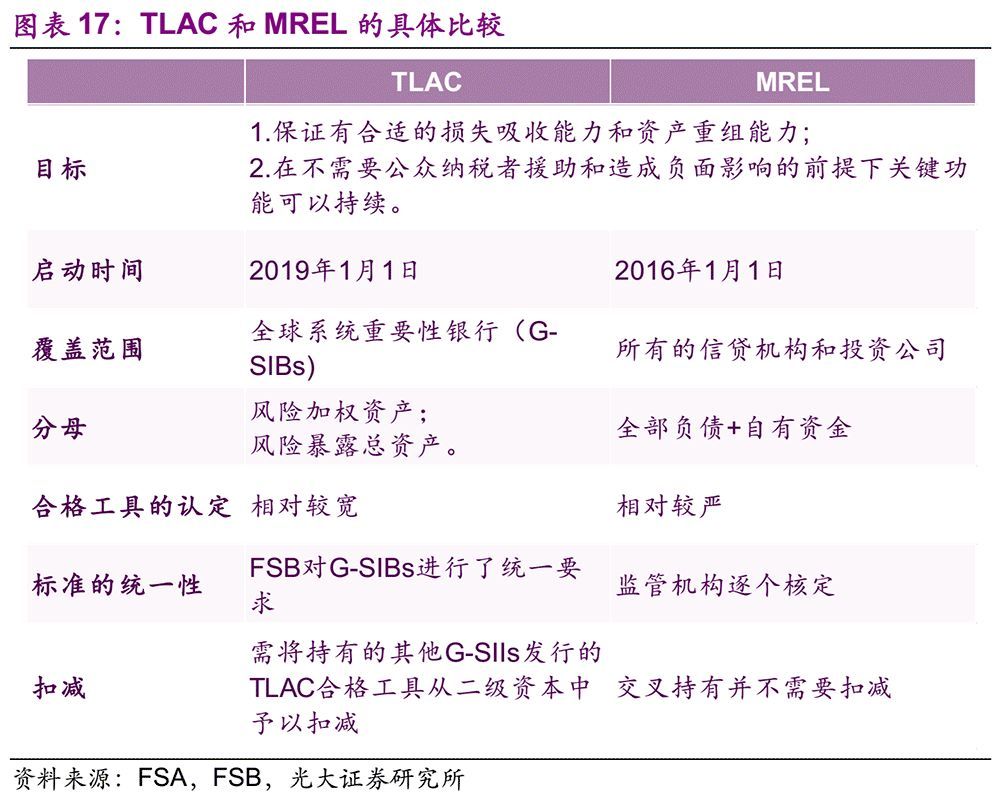
Similar to the TLAC of FSB, the European Union has put forward the Minimum Requirements for Self-owned Funds and Qualified Liabilities (MREL), which was implemented on January 1, 2016. The difference between MREL and FSB minimum TLAC requirements is mainly reflected in the following six points:
1. Different startup time: MREL requirements were implemented on January 1, 2016; The requirements of TLAC were implemented on January 1, 2019.
2. Different coverage: TLAC is only for G-SIBS; MREL covers all credit institutions and investment companies in the EU.
3. The denominators of the indicators are different: the denominators of the two indicators in TLAC are risk-weighted assets and total risk exposure assets respectively; MERL contains all liabilities and self-owned funds.
4. The criteria for identifying qualified debt instruments are different: when the debt instruments in MREL are converted into shares or written down during self-rescue, they must conform to the principle of "no credit or worse off (NCWO)", so the qualification identification is stricter than the TLAC standard of FSB.
5. The uniformity of standards is different: FSB has uniform minimum TLAC requirements for all G-SIBs; MREL determines the specific requirements of each bank on a case-by-case basis.
6. Different deductions: under the framework of TLAC, it is necessary to deduct the TLAC qualified tools held by other G-SIIs from Tier 2 capital; The current version of MREL framework does not involve deduction for the time being.
6. TLAC gap of G-SIBs
6.1. Current global TLAC compliance of G-SIBs.
Up to now (note: July 26, 2019), six countries or regions, including the United States, Britain, Japan, Canada, Switzerland and China, have met the external TLAC requirements. Among them, TLAC supervision in Japan began on March 31, 2019, which is slightly different from January 1, 2019 required by FSB. The EU MREL framework has been put into operation, which covers not only G-SIBs, but also D-SIBs and other banks.
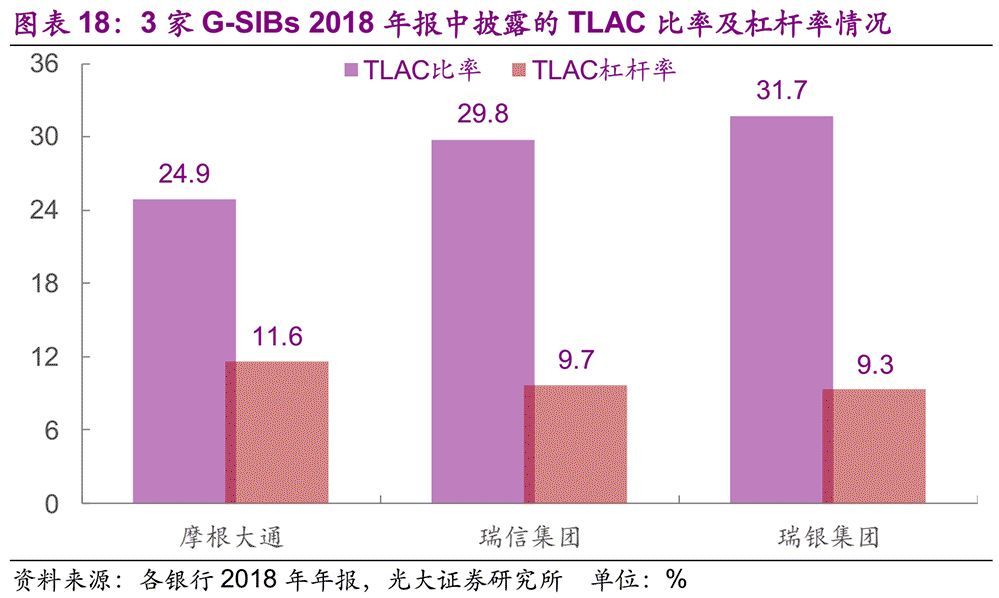
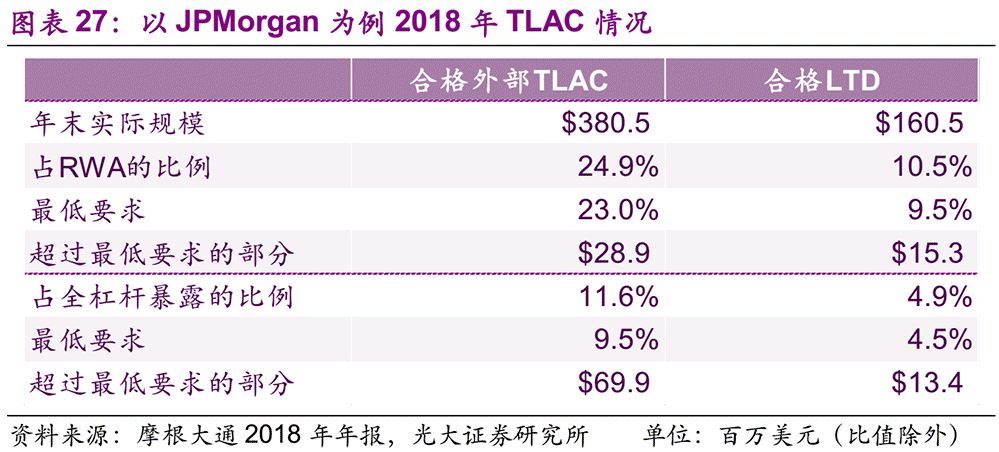
At present, some G-SIBs have disclosed their TLAC ratio and leverage ratio in their 2018 annual reports, such as JPMorgan Chase, Credit Suisse Group and UBS Group AG. These three banks have met the minimum TLAC requirements stipulated by FSB, while JPMorgan Chase has also met the stricter TLAC rules formulated by the United States.
6.2. TLAC gaps of four G-SIBs in China.
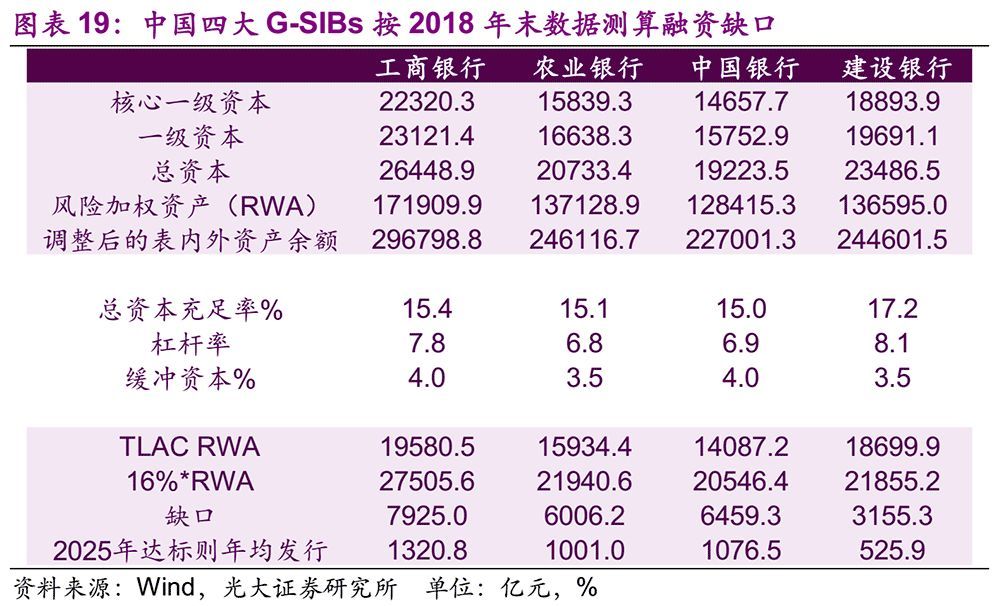
The TLAC Clause requires G-SIBs to meet the corresponding regulatory requirements from January 1, 2019, but gives emerging market countries a grace period of six years, so China has not yet implemented TLAC regulation. Because China’s G-SIBs has not issued corresponding TLAC debt instruments for TLAC rules, the TLAC ratio is close to the capital adequacy ratio after deducting the capital buffer. By the end of 2018, the average capital adequacy ratio of the four major banks of industry, agriculture, China and construction was 15.67%, and the capital adequacy ratio after deducting the capital buffer was 11.92%, which was still far from the regulatory ratio of 16%.
In terms of leverage ratio, by the end of 2018, the leverage ratios of ICBC, Agricultural Bank, Bank of China and China Construction Bank were 7.8%, 6.8%, 6.9% and 8.1% respectively, all of which were higher than 6%, and the leverage ratio pressure was relatively small.
Based on the calculation results of leverage ratio and TLAC ratio, the total TLAC financing gap of four G-SIBs in China at the end of 2018 was 2.35 trillion yuan. According to the current capital and operation of the four banks, if we want to meet the minimum TLAC requirements in 2025, we need to increase the TLAC by 392.4 billion yuan annually in the next six years.
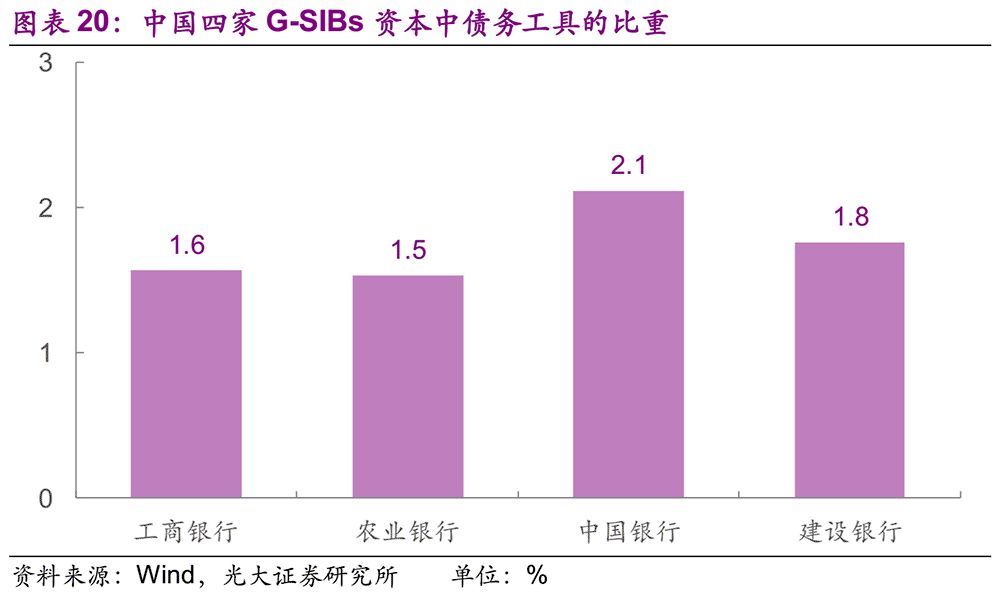
The regulatory expectation is that TLAC debt instruments that meet the standards account for no less than 33% of the total capital of TLAC. According to the minimum external TLAC requirement of 16%, debt instruments such as convertible bonds, perpetual bonds, subordinated bonds, mixed capital bonds and tier 2 capital instruments are not less than 5.28% of RWA’s. By the end of 2018, the above-mentioned debt instruments issued by the four major banks accounted for an average of 1.75% of RWA, which was significantly lower than the above-mentioned regulatory expectation of 5.28%. It is necessary to continue to promote the issuance of debt instruments.
7. Ways to promote TLAC standards
There is not much time for the TLAC of four G-SIBs in China to reach the standard. In terms of the time limit for TLAC to reach the standard, although China has been granted a grace period of six years, there is a big TLAC capital gap among the four G-SIBs, so the replenishment pressure of TLAC capital is enormous. How can we supplement TLAC as soon as possible to meet the requirements in the TLAC Clause? We believe that existing capital replenishment tools can be used to supplement regulatory capital, and debt instruments that are not included in regulatory capital but meet the requirements of TLAC can be issued.
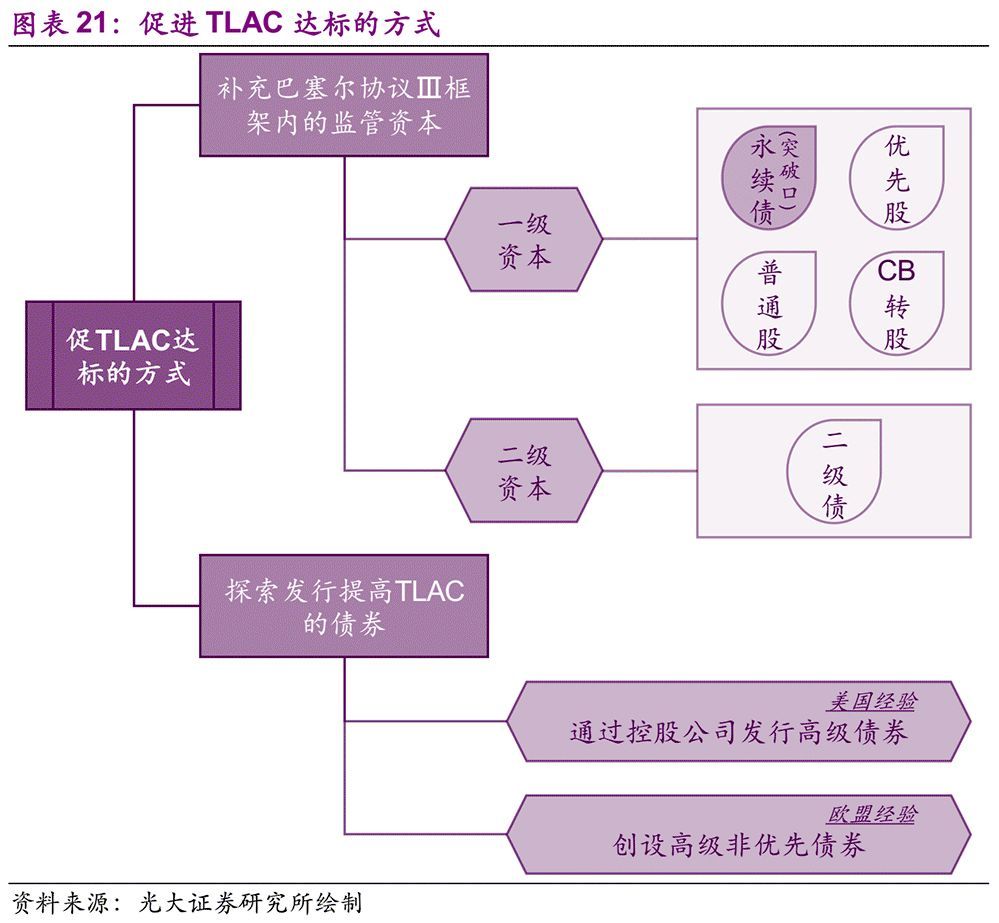
7.1. Supplementary regulatory capital within the framework of Basel III
The TLAC of commercial banks consists of two parts: one part is the regulatory capital of Basel III, and the other part is the TLAC debt instruments that meet the requirements outside the regulatory capital. Obviously, supplementing the regulatory capital of Basel III can not only improve the capital adequacy ratio, but also improve the TLAC, thus killing two birds with one stone.
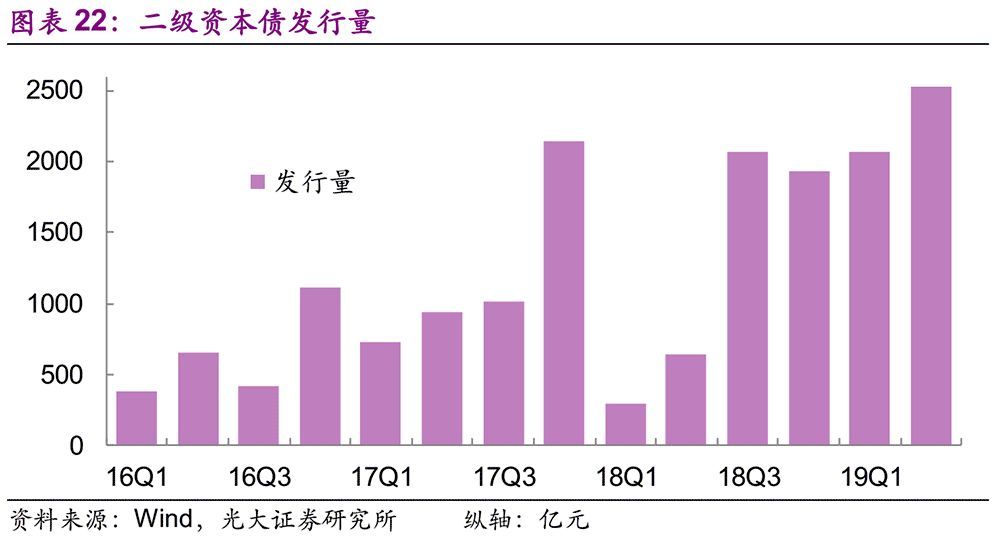
Compared with tier-one capital, tier-two capital is more convenient to replenish. In 2017 and 2018, China’s commercial banks issued 482.4 billion yuan and 493.7 billion yuan of tier-two debt respectively, which effectively supplemented tier-two capital. For Tier-1 capital, the traditional supplementary methods are mainly to issue common shares, preferred shares and convertible bonds into shares. However, the approval process of these options is long, involving many departments, and may disturb the capital market, so they will be restricted by the regulatory authorities in the issuance process.
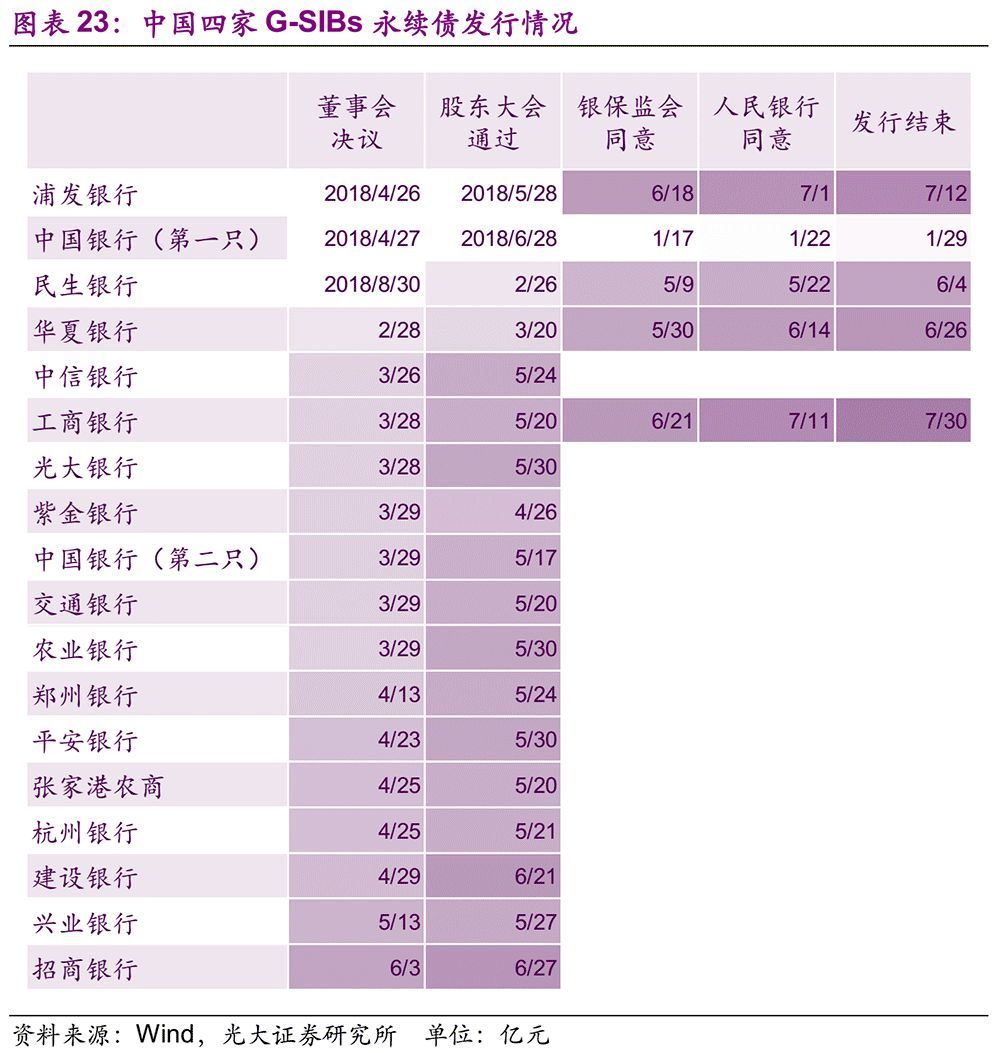
Perhaps, the perpetual bonds of commercial banks can be a breakthrough to supplement tier-one capital. At the end of January this year, China Bank successfully issued 40 billion yuan of write-down bonds with no fixed term, which is the first issuance of perpetual bonds of Chinese commercial banks in the interbank market. Up to now (July 26th), among the four G-SIBs in China, BOC and ICBC have issued 120 billion yuan of write-down perpetual bonds, and a total of 200 billion yuan of perpetual bonds of BOC, ABC and CCB have passed the shareholders’ meeting and can be issued after obtaining the approval from China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission and the People’s Bank of China.
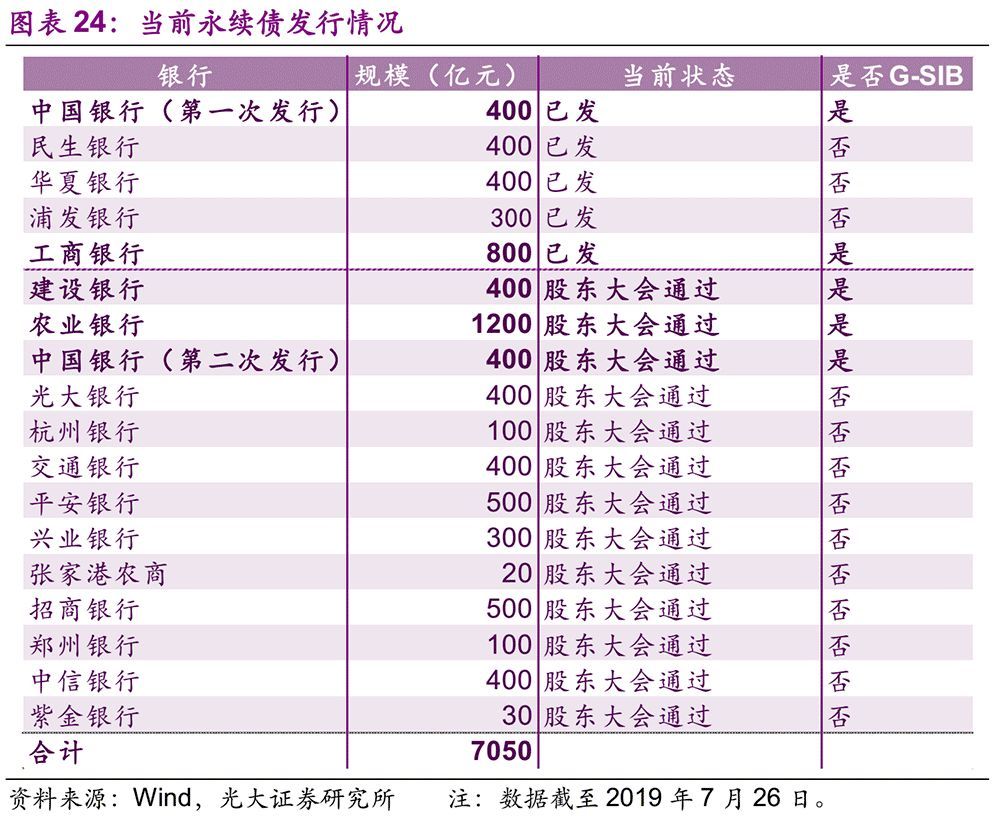
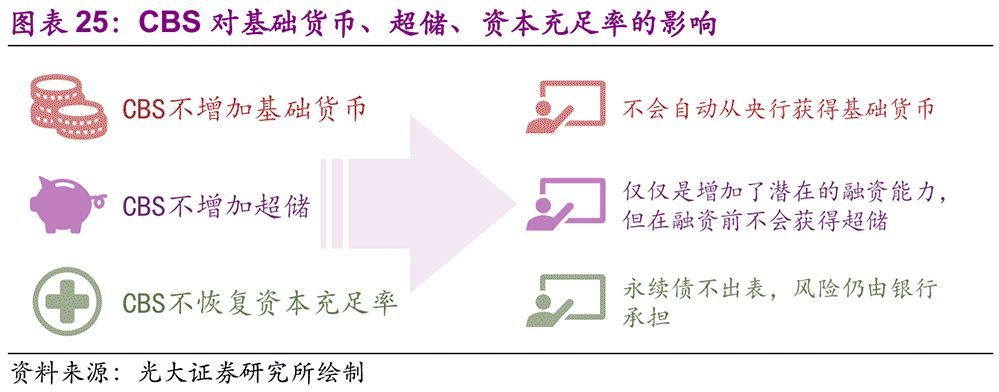
In order to issue perpetual bonds smoothly, the People’s Bank of China and China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission have also formulated relevant policies. On January 24, the People’s Bank of China decided to create CBS, so that primary dealers in the open market can use the perpetual bonds issued by qualified banks held by them to exchange them for central bank bills. Since then, the People’s Bank of China has launched CBS operation three times on February 20th, June 27th and the end of July to support banks to issue perpetual bonds to replenish capital. In addition, the People’s Bank of China will include the perpetual bank bonds with the subject rating of not less than AA into the eligible collateral of MLF, TMLF, SLF and refinancing. In essence, these two policies use the liquidity creation function of the People’s Bank of China to improve the potential financing ability of perpetual bonds investors, provide liquidity support for the issuance of perpetual bonds and reduce the issuance cost of perpetual bonds. It is worth mentioning that the above two policies introduce positive incentives, which are more sustainable than the traditional negative incentives of administrative orders.
7.2. Explore the issuance of bonds to improve TLAC.
In addition to using existing tools to supplement regulatory capital, TLAC can also be supplemented by some innovative capital tools. On January 18, 2018, the former China Banking Regulatory Commission, the People’s Bank of China, the China Securities Regulatory Commission, the former China Insurance Regulatory Commission and the Foreign Exchange Bureau jointly issued the Opinions on Further Supporting the Innovation of Capital Instruments of Commercial Banks (Y.J.F. [2018] No.5), proposing to "summarize the practical experience of commercial banks in issuing preferred stocks and write-down tier 2 capital bonds, promote the revision of relevant laws and regulations, study and improve supporting rules, and issue open-ended capital bonds and write-down tier 2 capital bonds for commercial banks. On February 28th, 2018, the People’s Bank of China issued Announcement [2018] No.3 of the People’s Bank of China, encouraging banking financial institutions to issue new capital supplementary bonds with innovative loss absorption mechanisms or triggering events, and clarifying that "banking financial institutions can explore issuing bonds to improve their total loss absorption capacity".
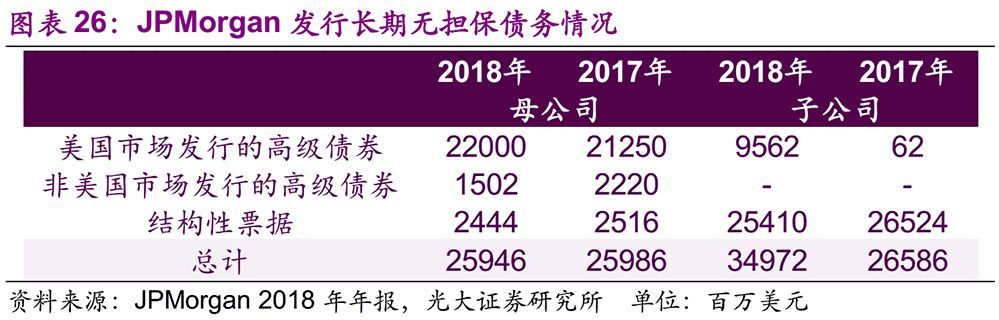
In the innovation of TLAC qualified tools, other countries have a lot of experience to learn from. Most banks in the United States meet the regulatory requirements of TLAC by issuing senior bonds by holding companies. For example, JPMorgan disclosed in its annual report that the company has a large number of long-term unsecured debts issued by the parent company to provide maximum flexibility to support the financing needs of banks and non-bank subsidiaries. JPMorgan, the mode of supplementing TLAC by issuing bonds from non-operating holding companies, is the secondary structure mentioned above. In this mode of secondary structure, the excluded liabilities of subsidiaries are paid off first, and the bonds of holding companies play the role of loss absorption.
Banks in EU countries tend to use "senior non-priority bonds" to supplement TLAC capital. In order to coordinate the EU’s regulations on the hierarchy of bank creditors and promote the formation of a disposal plan for cross-border institutions, the European Commission finally decided to choose the "French model" as the EU standard in November 2017. The "French model" adds the bond varieties of "Non-Preferred Senior Debts" as qualified TLAC tools in the traditional creditor rank sequence by agreeing on the secondary.
The repayment order of senior non-priority bonds is between subordinated debt and senior unsecured debt, which is superior to subordinated debt in grade, but inferior to senior unsecured debt, that is, a new interlayer is added on the basis of the existing debt structure. When issuing senior non-priority bonds, banks in the European Union need to meet the following agreements:
1) The original contract term is at least one year;
2) Bills cannot be derivatives and cannot contain embedded derivatives;
3) The relevant contract documents must clearly stipulate that the repayment order of debts is between subordinated debts and senior unsecured debts.
8. Summary
The disposal of the contractor bank has also triggered our new thinking: the failure of commercial banks has negative macro-spillover, and in order to prevent systemic risks, the government has to use public funds to provide assistance. Then, is it possible to put forward higher regulatory requirements for banks, so that they can reserve enough internal bail-out funds to absorb losses during the disposal process, instead of relying on external public funds for assistance?
In fact, in order to solve the problem of "negative macro spillover", the FSB (Financial Stability Board) has released "Key Elements of Effective Disposal Mechanism of Financial Institutions" at the G20 Cannes Summit in 2011, proposing the goal of "internal bail-out" instead of "external assistance" of public funds when in crisis. In November, 2015, FSB issued the Principles and Clauses of Loss Absorption and Capital Reorganization Ability in the Disposal of G-SIBs (referred to as TLAC Clause), which put forward higher requirements for the loss absorption ability of G-SIBs (global systemically important bank) than Basel III.
The above-mentioned "TLAC" is the abbreviation of Total Loss-Absorbing Capacity, which refers to the sum of various capital or debt instruments that can absorb bank losses through write-down or share conversion when G-SIBs enters the disposal procedure, that is, the ability of "internal bail-out". A higher TLAC ensures that banks have sufficient capacity to absorb losses when they enter the disposal procedure, thus reducing the probability that "too big to fail" banks will "fail" in a crisis and cause systemic risks. In addition, the "internal bail-out" model helps to encourage bank shareholders and management to increase risk management and reduce the possibility of excessive risk taking and falling into crisis.
Basel III applies to all banks, while the minimum TLAC requirements of FSB apply to G-SIBs. The minimum TLAC requirements include TLAC requirements based on risk-weighted assets and TLAC requirements based on risk-exposed total assets (i.e. leverage ratio). In addition to the above-mentioned mandatory provisions, FSB also put forward the regulatory expectation in the TLAC Clause, that is, it is expected that the standard TLAC debt instruments will account for no less than 33% of the total capital of TLAC. In addition to the requirements of FSB, the regulatory authorities of various countries or regions may put forward additional requirements for banks according to local actual conditions, and the specific standards shall be decided by the local regulatory authorities themselves.
The TLAC Clause requires that for banks that become G-SIBs before the end of 2015, the TLAC shall account for no less than 16% of risk-weighted assets and the leverage ratio shall be no less than 6% from January 1, 2019; From January 1, 2022, the above two proportions will be increased to 18% and 6.75% respectively. Considering the actual situation of emerging market countries, FSB gives them a grace period of six years, that is, the time to meet the standards is extended from 2019 and 2022 to 2025 and 2028. However, there is an accelerated condition for this grace period: if the balance of financial and non-financial corporate bonds (excluding policy banks) in emerging market countries accounts for more than 55% of the country’s GDP within five years after the publication of the TLAC Clause, the grace period will be shortened by three years and advanced to 2022 and 2025 respectively.
In December 2016, the Federal Reserve finalized the American version of the TLAC rules, which are applicable to the global systemically important bank holding companies (covered BHCs) in the United States and the important intermediate holding companies (covered IHCs) of foreign banks in the United States. The US TLAC rules formulated by the Federal Reserve are obviously stricter than the requirements of the FSB.
In the TLAC requirements formulated by the Financial Services Agency of Japan (FSA), it is considered to extend the scope of supervision to some D-SIBs, such as Nomura Holdings, Daiwa Securities, Japan Central Agriculture and Forestry Treasury, and Sumitomo Mitsui Trust Holding Company. In addition, Japan’s TLAC rules have been implemented since March 31, 2019, which is slightly different from January 1, 2019 stipulated by FSB.
Similar to the TLAC of FSB, the European Union has put forward the Minimum Requirements for Self-owned Funds and Qualified Liabilities (MREL), which was implemented on January 1, 2016. The difference between MREL and FSB’s minimum TLAC requirements is mainly reflected in the following six points: start-up time, coverage, denominator of indicators, identification standard of qualified debt instruments, unity of standards and deduction items.
There is not much time for the TLAC of four G-SIBs in China to reach the standard. In terms of the time limit for TLAC to reach the standard, although China has been granted a grace period of six years, there is a big TLAC capital gap among the four G-SIBs, so the replenishment pressure of TLAC capital is enormous. How can we replenish TLAC capital as soon as possible to meet the requirements in the TLAC Clause? We believe that existing capital replenishment tools can be used to supplement regulatory capital, and innovative debt instruments that are not included in regulatory capital but meet the requirements of TLAC can be issued.
The TLAC of commercial banks consists of two parts: one part is the regulatory capital of Basel III, and the other part is the TLAC debt instruments that meet the requirements outside the regulatory capital. Obviously, supplementing the regulatory capital of Basel III can not only improve the capital adequacy ratio, but also improve the TLAC, thus killing two birds with one stone. Perhaps, the perpetual bonds of commercial banks can be a breakthrough to supplement tier-one capital. At the end of January this year, China Bank successfully issued 40 billion yuan of write-down open-ended bonds, and Industrial and Commercial Bank of China also issued 80 billion yuan of open-ended bonds. In order to issue perpetual bonds smoothly, the People’s Bank of China and China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission have also formulated relevant policies. For example, the People’s Bank of China has created CBS, and primary dealers can use the perpetual bonds issued by qualified banks held by them to exchange them for central bank bills.
In addition to using existing tools to supplement regulatory capital, TLAC can also be supplemented by some innovative capital tools. In the innovation of TLAC qualified tools, other countries have a lot of experience to learn from. Most banks in the United States meet the regulatory requirements of TLAC by issuing senior bonds by holding companies, while banks in EU countries tend to use "senior non-priority bonds" to supplement TLAC capital.
9. Risk warning
If the standard of qualified TLAC debt instruments applicable to China is not clear for a long time, it will not be conducive to the four G-SIBs to supplement TLAC, and ultimately have a negative impact on the ability of finance to support the real economy. In addition, the centralized issuance of TLAC tools will also test the affordability of the bond market to some extent.
This article first appeared on WeChat WeChat official account: EBS fixed income research. The content of the article belongs to the author’s personal opinion and does not represent Hexun.com’s position. Investors should operate accordingly, at their own risk.
(Editor: Li Jiajia HN153)